Currently, nationwide effort is on-going to vaccinate the population in Malaysia, including children, against COVID-19. What is the current status of childhood immunisation programme in Malaysia?
The past
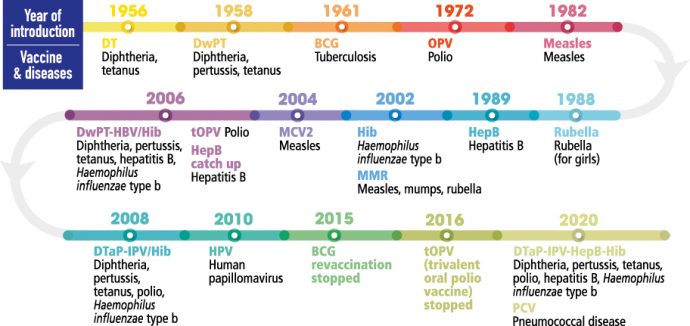
Timeline of paediatric vaccine introduction in Malaysia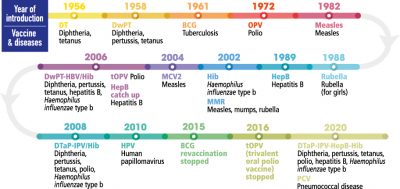
The National Immunisation Programme (NIP) for children in Malaysia was first initiated in the early 1950s with the introduction of the smallpox vaccine. More vaccines have been included since then, and currently, our immunisation coverage is considered high at >95%. The NIP provides free vaccination for all children; though starting in 2015, non-Malaysians have to pay a minimal fee. Since the NIP was established in our country, the prevalence of diseases covered has reduced significantly.
The present: 6-in-1 vaccine and PCV
There are 2 most recent updates to the NIP: 1) the switch from the 5-in-1 vaccine to the 6-in 1 vaccine, 2) the introduction of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV).
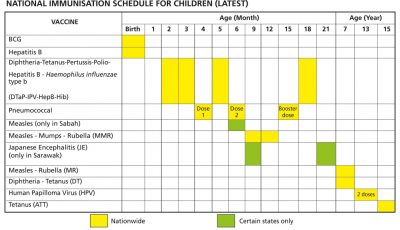
In November 2020, the Ministry of Health introduced the 6-in-1 or hexavalent vaccine to replace the 5-in-1 or pentavalent vaccine used previously. The 5-in-1 (DTaP-IPV/Hib) vaccine provided protection against diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio and Haemophilus influenzae type b and was given in 3 primary doses at age 2 months, 3 months and 5 months, plus a booster dose at age 18 months.
Now, the 6-in-1 (DTaP-IPV-HepB-Hib) vaccine will also provide protection against Hepatitis B, in addition to the other 5 diseases. The same number of doses will be given at same ages (2, 3, 5 and 18 months). The monovalent Hepatitis B (HepB) vaccine, which was previously given at birth, age 1 month and age 6 month, will be given only in 1 dose at birth now.
The switch resulted in a reduction of the number of shots required to cover the 6 diseases, from 7 to only 5 shots. This helps parents to ensure that their child receives timely vaccination according to the schedule as there will be less injections and less visits to the clinic. The reduced number of injection also means less pain and discomfort to the child.
Then, in December 2020, the pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) was finally included in the NIP after the budget was approved in the previous year. PCV10, which protects against pneumococcus serotypes 1, 4, 5, 6B, 7F, 9V, 14, 18C, 19F and 23F, will be given in 3 doses – 2 primary doses at age 4 months and 6 months and a booster dose at age 15 months. However, only children born in 2020 or later are eligible for the free PCV shots in the NIP. Regardless, this is a significant improvement for the NIP.
The current NIP schedule
COVID-19 vaccination for children and adolescents
COVID-19 vaccination for the adolescent group (12-17 years old) was initiated in September 2021, where 2 standard doses are given at least 21 days apart. At the time of writing, more than 90% of adolescents in Malaysia have received both doses.
Meanwhile, COVID-19 vaccination for children (PICKids) aged between 5 to 11 years has also started in February 2022. 2 doses will be given in an 8-week interval. A smaller paediatric dose is given, which is equivalent to 1/3 of the standard dose.
The future
The NIP for children in Malaysia currently provides protection against 13 diseases: tuberculosis, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, Haemophilus influenzae type b, Hepatitis B, human papillomavirus, measles, mumps, rubella, Japanese encephalitis (Sarawak only) and the latest, pneumococcal disease.
There are still other additional recommended vaccines for children, such as rotavirus, meningococcal, chicken pox, Hepatitis A and influenza vaccines. These vaccines may be proposed for future inclusion in the NIP if deemed necessary.
However, the rise of anti-vaccination movement recently, especially in opposition to the COVID-19 vaccination drive, may disrupt the effort in improving our immunisation programme. Among the solutions proposed to counter this challenge is to implement mandatory vaccination. However, it is also crucial to continue educating the public about the importance of vaccination.




Comments