A child’s overall growth and development is, among other things, largely dependent upon nutrition. An optimum and balanced amount of various nutrients ensures your child grows normally and healthily. Similarly, it provides:
- Protection for your child against various illnesses, diseases and infections by strengthening the body and immune system.
- Energy required to keep up with a child’s rapid development both physically and mentally.
- Good physical and mental development such as better memory, good vision and improved attentiveness in school.
No single food alone can meet your child’s entire nutritional needs. The child’s body performs various functions (i.e. digestion, cognitive function, muscle contraction, bone hardening) and growth is rather rapid during this period. Hence, different nutrients are needed to fulfil these different needs.
Nutrient Intake For Children
Calories consumed daily should come from a variety of sources so that the child gets the required and appropriate amount of nutrients his/her body needs to grow. Some of the key nutrients, their functions and sources include:
NutrientFunctionRich Sources
| Calcium | Builds strong bones and teeth, promotes healthy nerve and muscle function, helps blood clot, and helps with keeping a normal heartbeat. | Milk, yoghurt, cheese and dairy products, canned sardines, anchovies, tofu and tempeh, spinach, kailan and broccoli |
| Iron | Important for making haemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying red pigment in blood, and myoglobin, a pigment that stores oxygen in muscles. | Lean beef, meat, chicken, egg, fish, liver, green leafy vegetables such as spinach, kangkung, kailan |
| Magnesium | Keeps bones strong and the heart rhythm steady, supports the immune system, and helps maintain muscle and nerve function. | Seaweed, beans, nuts and seeds (almonds, sunflower and sesame seeds), as well as avocados |
| Zinc | Needed by enzymes that aid digestion and metabolism, and essential for growth. | Meat (beef, pork), poultry, fish and shellfish. Nuts, seeds, legumes and whole grain cereals (especially bran and germ) |
| Vitamin A | Plays an important role in vision and bone growth; helps protect the body from infections; promotes the health and growth of cells and tissues in the body, including the hair, nails, and skin. | Liver, eggs, papaya, mangoes, carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkin, green leafy vegetables such as spinach, kangkung, kailan |
| Vitamin D | Helps the body absorb minerals like calcium and builds strong teeth and bones. Essential for reaching growth potential and peak bone mass. | Fish liver oils, fortified cow milk, canned sardines, chicken liver and egg yolk |
| Vitamin E | Limits the production of free radicals, which can damage cells. Important for immunity, DNA repair, and other metabolic processes. | Palm oil, rice bran oil, and the bran and germ portions of cereals such as oat, barley and rice |
| Iodine | Used by the thyroid gland to help regulate metabolism and development of both the skeleton and brain. | Seaweeds, marine fishes and shellfish |
| Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) |
Needed for energy metabolism, building tissue, and helps maintain good vision. | Milk, liver, chick peas, lentils, eggs, and beef |
| Niacin (Vitamin B3) |
Essential for converting food to energy. It supports the function of the digestive system, skin and nerves, and improves circulation. | Beef, liver, pork, fish, anchovies, nuts, whole grains and whole-meal wheat flour |
For infants, breastmilk provides all the necessary nutrients they require. It is recommended that infants are exclusively breastfed until they are 6 months old. Continued breastfeeding until 2 years and coupled with complementary feeding is also highly encouraged.
The B.M.V Approach
The fundamental of good nutrition is to be balanced in the type of foods you choose for your kids, have them eat moderate portions at every meal and provide them with a variety of foods with different textures, colours and tastes.
What should I give and how much?
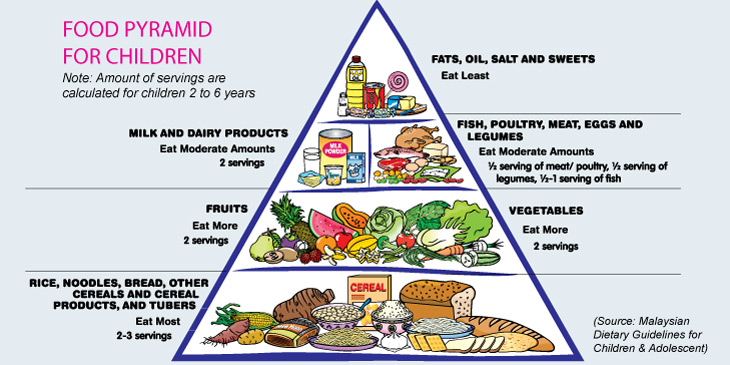
Following the approach, eating various types of foods at every meal ensures your child gets all the various nutrients he/she needs. The Food Pyramid for Children (2-6 years) can help you prepare balanced meals for your child. Remember to keep portion sizes moderate.
Practice Healthy Eating Habits As A Family
When the whole family is willing to be on board towards good eating habits and a healthy diet, the practice becomes a routine everyone eventually gets used to.
Additionally, you should try:
- To reduce use of fats, salt and sugar when cooking
- Read nutrition labels before buying your foods
- Use healthier cooking methods (e.g. stewing, boiling, roasting)
- Eat together as a family during main meals to promote bonding
- Not skipping meals.
Make sure you involve your child in these practices. Let him/her know why the family is making these choices. The more informed your children are the better they are at making the right choices in the food they eat.






Comments