You may think that your child should avoid fat in his diet because as most people will tell you, fat is bad for health and will only cause Junior to become obese. Contrary to popular belief, however, your child does need fat in order for his body to function properly. It’s only when your young one gets too much fat that health problems begin.
Why Your Child Needs Fat
Fat is important for your child as it aids nutrient absorption, nerve transmission and maintains cell membrane integrity. Besides being a source of energy, it also helps maintain healthy hair and skin, protects vital organs and keeps the body insulated by preserving heat to maintain body temperature.
Fat functions in your child’s body in these ways:
- As an essential component for the functioning of healthy membranes
- Insulates and acts as a shock absorber for bones and organs
- Provides hormone-like substances to regulate many bodily functions
- Omega-3 fatty acids assist in growth, development and brain function
- Helps the body absorb fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and K
- Provides structural components of myelin, the fatty insulating sheath surrounding each nerve fibre, enabling it to carry messages faster
Types of Fatty Acids
Chemically known as fatty acids, FAs are known simply as fat. Fatty acids can be categorised into 3 basic groups: monounsaturated fats (MUFAs), polyunsaturated fats (PUFAs) and saturated fats (SFAs)
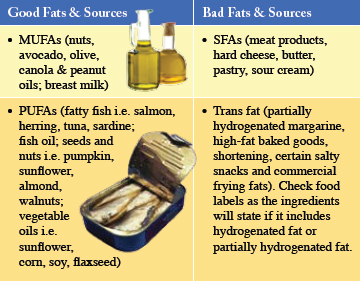
MUFAs and PUFAs (including essential fats like Omega-3 and Omega-6) are known as good fats and are neutral and beneficial to heart health. SFAs and trans fats (also referred to as trans-fatty acids) are harmful fats. Too much saturated fats increase the amount of cholesterol in the blood.
| What are EFAs? |
|---|
|
Fat also provides essential fatty acids (EFAs) needed for specific body functions. EFAs are the building blocks of brain development and the main nutritional component of fats. The body requires many different types of acids and can make all, except alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of Omega-3 fatty acids, and linoleic acids (LA), a type of Omega-6 fatty acids, which must come from your child’s food. EFAs support healthy brain development from baby to teenage years, support the development of eyes, skin and joints and maintain healthy cholesterol levels. They also promote good circulation to maintain a healthy heart and a healthy immune system. Now that you know that fat is essential for your growing child, do ensure your little one gets a variety of good fats in adequate amounts in his diet. Keep in mind that too much fat leads to obesity and health problems. Focus on reducing foods high in saturated fats and trans fats and select more foods containing unsaturated fats. |






Comments